Hybrid Cable: What You Should Know
What is hybrid cable ?
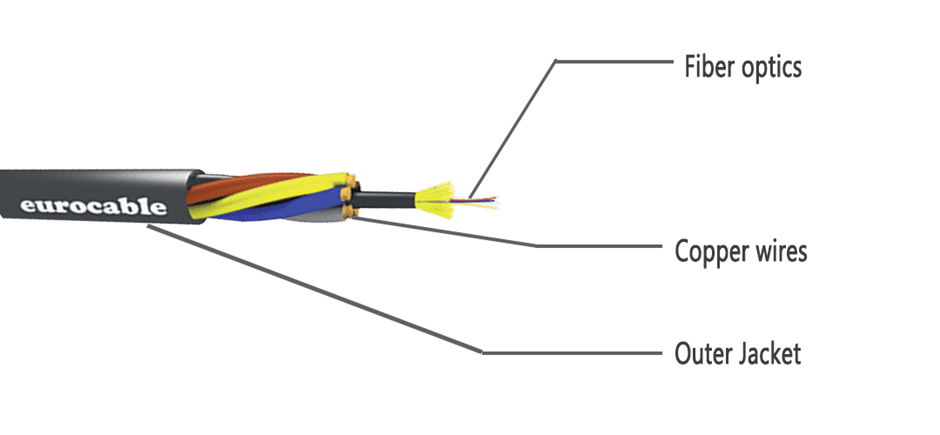
A hybrid cable combines optical fibers and copper wires within the same jacket and serves as a power supply and data transmission medium. This is why hybrid cables are commonly used on campus networks to connect switches and APs or switches and remote units. As future-proof WLAN technologies such as Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 gain traction, conventional twisted pairs are unable to meet their bandwidth requirements. Furthermore, optical fibers are not suitable for PoE power supply. This is where a hybrid cable comes into play.
What Is the Purpose of Hybrid Cables?
Generally, we use two types of wired media in networks there are Copper cable and Fiber optic cable.
To ensure the smooth operation of network services, cables between devices must perform two functions: power supply to devices and data transmission between devices. With the introduction of PoE (power over Ethernet) devices, the power supply and data transfer to the device are done with a single copper cable. But copper cables can only send a distance of hundreds of meters. It’s main disadvantage in copper cable. Fiber was used as a solution for that.
However, some network devices, such as WLAN APs, 5G base stations, and video surveillance cameras, must be installed in complex environments where proper receptacles are difficult to find. To overcome this, a single cable that can serve as both a power supply and a data transmission medium becomes essential.
Based on their transmission media, communication cables are typically classified as optical cables or copper cables. To elaborate, optical fibers are most commonly used to transmit light based on total internal reflection, and they have benefits such as high bandwidth, low loss, and long transmission distance. However, because they are made of glass fibers, which cannot conduct electricity, they cannot be used for PoE power supply. Copper cables are made up of copper wires that send data via electromagnetic waves. Copper cables, as a good conductor of electricity and heat, can transmit both data and electrical signals, but will heat up quickly in the process. This can result in significant transmission loss, so copper cables are not suitable for long-distance transmission. To avoid this, network integrated cabling regulations state that the total length of twisted pairs should not exceed 100 m. Faced with this challenge, we must create a cable that can serve as a medium for PoE power supply while not impeding long-term bandwidth evolution. This is where a hybrid cable comes into play. Hybrid cables combine the advantages of common copper cable and the advantages of fiber cable.
Advantage of Coper cable
- Cost: Twisted pair cables are significantly less expensive than fiber optic cables.
- Installation: Twisted pair cables are easier to install and terminate, making them a popular choice for home and small business networks.
- Flexibility: Twisted pair cables are more flexible and easier to route through tight spaces and around obstacles, compared to fiber optic cables.
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance: Twisted pair cables have a better resistance to electromagnetic interference, which makes them a good choice for environments with high levels of EMI.
- Availability: Twisted pair cables are widely available and have been used for many years, making them a well-established technology.
Advantage of fiber optic cable
- Bandwidth: Fiber optic cables have much higher bandwidth capacity than copper cables, allowing for faster data transfer rates and supporting more demanding applications.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them a good choice for environments with high levels of EMI.
- Distance: Fiber optic cables can support longer distances without signal degradation compared to copper cables, making them a good choice for long-haul communications.
- Security: Fiber optic cables are more secure than copper cables, as they are difficult to tap or eavesdrop on.
- Durability: Fiber optic cables are more durable and resistant to physical damage, as they do not rely on conductive materials to transmit data.
- Heat resistance: Fiber optic cables are able to operate in high temperature environments, making them a good choice for industrial and high-heat applications.
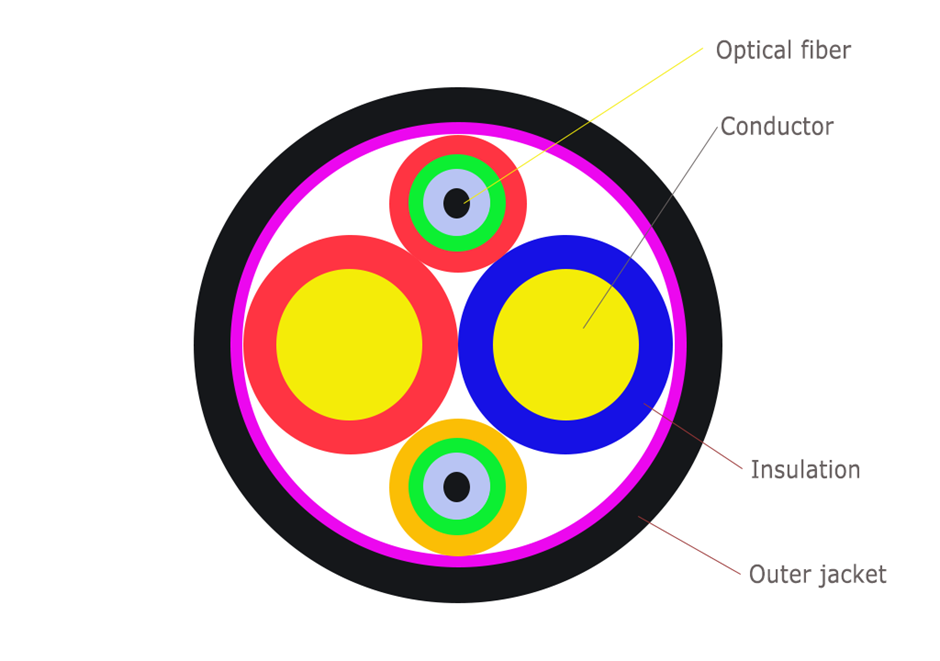
A hybrid cable is one that contains both optical fibers and copper wires within the same jacket. It transmits data signals via optical fibers and electrical signals via copper wires, allowing for long-distance power supply while maintaining high-speed data transmission. In a nutshell, this cable maximizes the benefits of optical fibers while minimizing the drawbacks of copper cables. The diagram below depicts the cross section of a hybrid cable. The hybrid cable uses a special fiber-copper incorporation structure and a custom protective layer to ensure that optical and electrical signals do not interfere with each other during transmission. Not only that, but it can be deployed in a variety of network systems, lowering network engineering and construction costs significantly.
Usage of hybrid cable
On campus networks, hybrid cables are commonly used to connect APs or remote units to switches, as illustrated in the figure below. Twisted pairs are commonly used to connect switches and APs and can serve as a medium for PoE power supply to APs and data transmission between switches and APs. However, as Wi-Fi technologies advance, they place ever-increasing demands on cable performance. For example, because Wi-Fi 6 is widely used commercially, the cable must support up to 10 Gbit/s of bandwidth. The Wi-Fi 7 standards also require the cable to deliver up to 40 Gbit/s of bandwidth while supporting PoE power supply to APs over long distances. Most APs are installed in complex environments and require PoE power supply over greater than 100 m distances. In some cases, the power supply distance will be much greater. For example, APs in some stadiums require power supply distances of 300 m or more. Traditional twisted pairs, on the other hand, can only support PoE power supply over a distance of up to 100 m. All of this demonstrates that hybrid cables are the best option for connecting switches and access points.
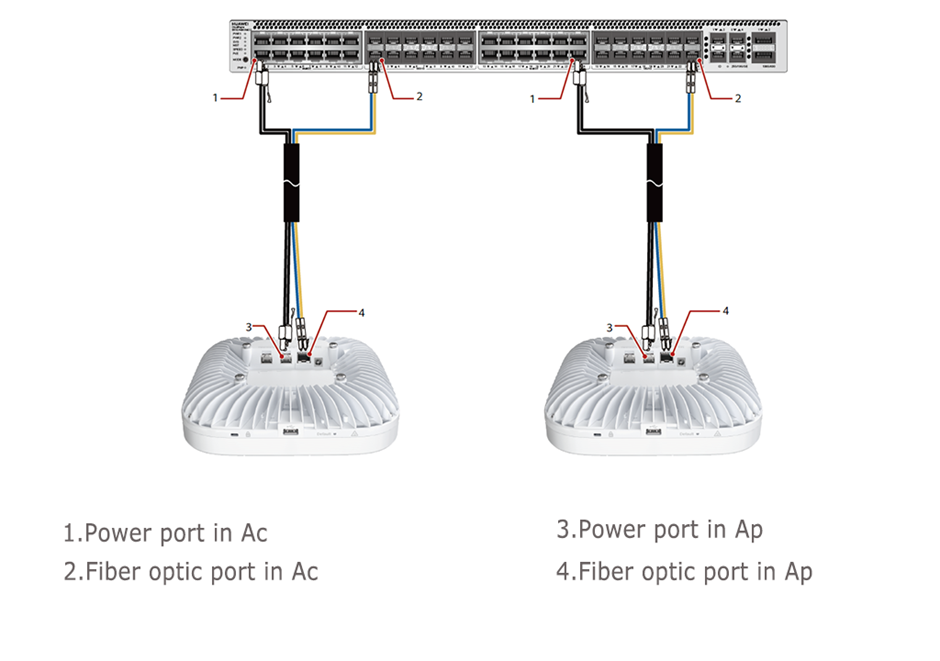
Other Usage of hybrid cable.
- Data centers: Hybrid cables can be used to provide both power and data connectivity in data centers and server rooms.
- Industrial settings: Hybrid cables can be used in industrial environments to provide both control signals and power to equipment.
- Medical equipment: Hybrid cables can be used in medical equipment to provide both power and data connectivity to medical devices.
- Home entertainment systems: Hybrid cables can be used in home entertainment systems to provide both audio and video signals as well as power to components.
- Automation systems: Hybrid cables can be used in automation systems to provide both control signals and power to industrial machinery.
- Security systems: Hybrid cables can be used in security systems to provide both power and data connectivity to security cameras and other components.
Generations of Hybrid Cable
Based on the connector type, hybrid cables are classified into two generations: hybrid cable 1.0 and hybrid cable 2.0. As illustrated in the figure below, hybrid cable 1.0 has separated optical-electrical connectors, whereas hybrid cable 2.0 has integrated optical-electrical connectors.
When connected to a device, hybrid cable 1.0 takes up both an electrical and an optical port. To be more specific, copper wires in such a cable must be terminated by an RJ45 connector before being inserted into the electrical port, whereas optical fibers must be terminated by a common LC connector before being inserted into a common commercial optical module on the optical port. The optical port is in charge of data transmission, while the electrical port is in charge of PoE power supply. When connected to a device, hybrid cable 2.0 takes up only one hybrid optical-electrical port. That is, before being inserted into a hybrid module via the hybrid optical-electrical port, the cable is fusion spliced with a pigtail or jumper with a PDLC connector. The hybrid optical-electrical port is in charge of data transmission as well as PoE power supply.
The primary distinction between hybrid cable 1.0 and hybrid cable 2.0 is that hybrid cable 2.0 can be connected to a hybrid optical-electrical port on a hybrid optical-electrical switch, allowing separated optical and electrical ports to be integrated into a single port. This enhancement simplifies fusion splicing and the use of hybrid cables while also doubling the density of optical and electrical ports. Hybrid cable 2.0 will take over in the near future.

Types of Hybrid Cable
1. Hybrid Fiber Coaxial (HFC) cable: A high-speed data transmission cable that combines optical fiber and coaxial cable.
2. Hybrid Audio Cable: A type of cable that transmits audio using both analog and digital signals.
3. Hybrid Control Cable: A cable that transmits control signals as well as power between electronic devices.
4. Hybrid Power Cable: A cable that combines electrical power and data signals into a single cable.

